All you need to know about ear infections in kids
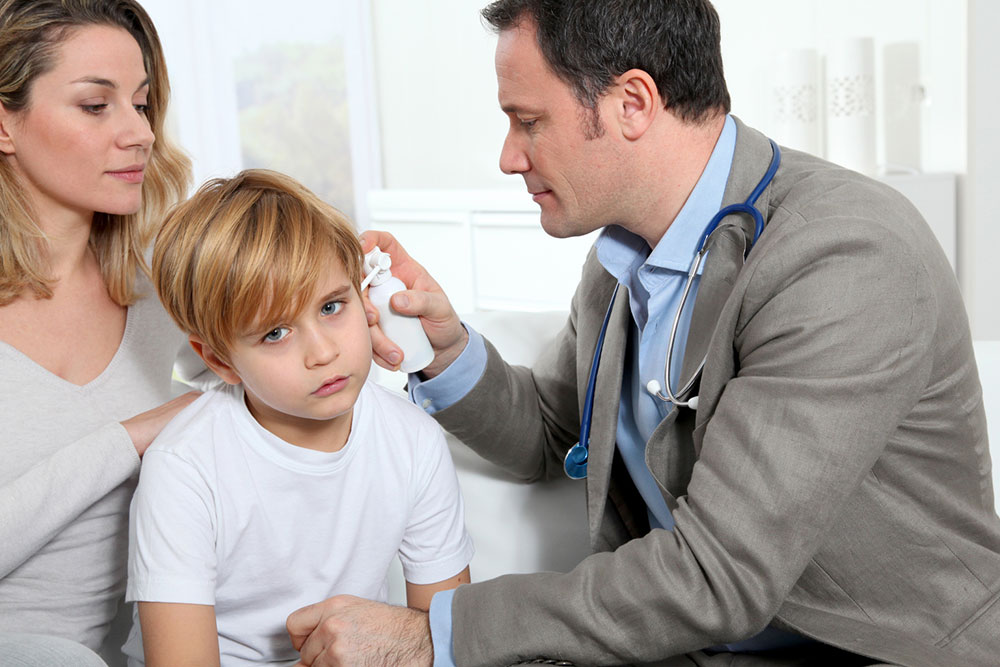
Ear infections, also called otitis media, is an inflammation in the middle ear which causes accumulation of fluid behind the eardrum. It can happen to anybody but is most commonly observed in children between the ages of 6 months to 3 years. Ear infections are usually not severe or contagious. However, timely diagnosis and treatment can prevent any discomfort. In most cases, ear infections occur when the child has had a cold for quite some time.
Causes
Generally, the cause of an ear infection is viral or bacterial infections. The thin Eustachian tube connects the middle ear with the back of the throat. In some cases, the Eustachian tube allows the passage of germs from the throat to the middle ear, especially when the child has a cold.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of ear infection in children are fever, issues with eating, sucking, chewing, and drinking. Ear infections also cause pain when a child lays down due to the pressure change in the middle ear.
Types of ear infections
- Acute otitis media: It is the most common type. It develops due to an infection of the middle ear and subsequent build-up of fluid behind the eardrum, leading to ear pain and fever.
- Otitis media with effusion (OME): It is a condition in which fluid remains trapped behind the eardrum. OME typically has no symptoms, but a specialist can see the accumulated fluid with the help of some medical devices.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion: In this type of ear infection, the fluid remains trapped in the middle ear for a long duration, and the problem recurs even when there is no ear infection. It affects hearing and the ability to fight new infections.
Risk factors for ear infections
Some common risk factors for ear infections are:
- Children below five years are more prone because their Eustachian tube is smaller.
- Children who attend daycare are highly susceptible as they come in contact with other children who may have a cold.
- Allergies can lead to ear infections.
- Children who have not undergone a proper breastfeeding period may face this problem. Breast milk contains antibodies which help kids fight infections.
Children who frequently come in contact with cigarette smoke are also at risk. - Exposure to this smoke causes inflammation in the Eustachian tube.
- In some children, milk enters the Eustachian tube when they are bottle fed. Due to this, they may face inflammation and infection in the middle ear.
- Children who are born with cleft palate have an inflamed Eustachian tube.
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose ear infections with the help of an otoscope which is an instrument used to analyze the eardrum. A doctor will observe the appearance of the eardrum, the pressure in the middle ear, and fluid accumulation.
Treatment
Depending on the situation, one can treat ear infections using antibiotics, eardrops, and pain-killers.
Ear infection in children occurs due to bacterial or viral infections of the middle ear and can cause inflammation and pain. Timely diagnosis and consultation will help in reducing the pain and discomfort that a child faces.