Diagnosis and treatment options for deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when there is a formation of a blood clot in a single or multiple deep veins in the body. This generally occurs in the legs, resulting in a swelling or leg pain, but it may also occur without any symptoms. It may be caused by certain conditions that form blood clots. It may occur when you are bound without much of a movement. Deep vein thrombosis may get extremely serious when the blood clots in the veins break loose and then pass through the bloodstream in the lungs, thereby restricting blood flow. In this article, we will talk about the diagnosis and the treatment options for this condition:
Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis
One of the first steps toward diagnosing deep vein thrombosis would be to scrutinize the symptoms you are suffering from. A physical examination may also follow to check the swellings, discoloration, and tenderness of the skin. Keeping in mind your proneness to getting a clot, the doctor may suggest some of the tests mentioned below:
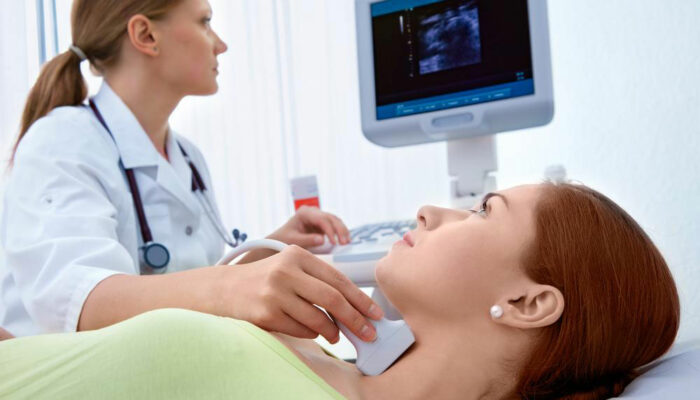
- Ultrasound
A transducer is placed above the particular part of the body where there is a clot in order to send sound waves inside the affected region. Once these waves travel, they reflect back. The computer goes on to transform the waves into a motion graphic or image on the screen. This will show if there is a clot or not. - Venography
To carry out this test, a dye is injected into the large vein in the foot or the ankle. This X-ray will create an image of these veins that may have clots. However, this is a more invasive method. A CT scan or an MRI scan may also be used for the same. - Blood test
Almost every person who develops deep vein thrombosis may have an elevated level of D-dimer in the blood, which is a protein fragment seen in the bloodstream after the degradation of a blood clot.
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis
The treatment for deep vein thrombosis aims at preventing the clot from becoming bigger in size. It also helps in stopping the clot from breaking loose and causes a pulmonary embolism to prevent deep vein thrombosis from occurring again. Some of the top treatment options for deep vein thrombosis are as shown below:
- Blood thinners
Deep vein thrombosis may be treated with blood thinners which are also known as anticoagulants. They are injectable in nature and some examples of this treatment include heparin, Lovenox, fondaparinux, and Fragmin. - Clot busters
In case of a more serious kind of deep vein thrombosis , blood thinners may not be enough. In such a case, medications will be used to break the clots. These are known as thrombolytics and may be given via intravenous measures. - Compression stockings
To prevent the swelling associated with this condition, compression stockings need to be worn on the legs, from the feet to above knee level. - Filters
In case your body does not permit you to intake medicines, then filters may need to be inserted into your abdomen. This helps in the prevention of clots, which break loose from lodging inside the lungs.