Lung cancer – Symptoms, causes, and treatment
As per recent medical statistics, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the country for men as well as women. Studies show that lung cancer has a higher fatality rate than many other cancers combined. While people who smoke regularly fall into a high-risk bracket for contracting lung cancer, there are many who have never touched a cigarette in their lives and have yet fallen a victim to this disease. Let’s take a look at the main causes of lung cancer, know the symptoms, and explore the diagnosis and treatment options available.
Types of lung cancer
There are two main types of lung cancer:
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): This is the type of cancer that affects chain-smokers. Only 10 to 15 percent of cancers fall under this category.
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): This term is used to refer to several types of lung cancers together, primarily because the treatment for most of them is similar. Some of the lung cancers that fall under this group are squamous cell carcinoma, bronchoalveolar, and large cell carcinoma.
Symptoms of lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease that shows its symptoms early on. Most of the main symptoms occur visibly in the advanced stages of the disease. The primary symptoms of lung cancer include the following:
- A constant cough that does not go away
- Coughing blood
- Hoarseness of voice
- Heaviness in the chest
- Sudden and inexplicable weight loss
- Bone pain
- A headache
- Muscle weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Confusion
- Pleural effusion (accumulation of fluids in the chest cavity)
Causes of lung cancer
Some of the causes of lung cancer are discussed below:
- Lung cancer is most commonly caused by smoking. When a person starts smoking, the cigarette smoke damages the lung tissue. The lungs repair the damage, but repeated exposure to cigarette smoke leaves the lung cells incapable of repairing the damage.
- Passive smoking is equally harmful to health.
- The exposure to certain substances over an extended period of time may also cause lung cancer. These substances include arsenic, cadmium, nickel, chromium, and uranium.
- In some cases, lung cancer is passed on genetically.
Diagnosis and treatment
On the evaluation of the physical symptoms, the doctor will prescribe certain tests to ascertain whether the patient is suffering from lung cancer:
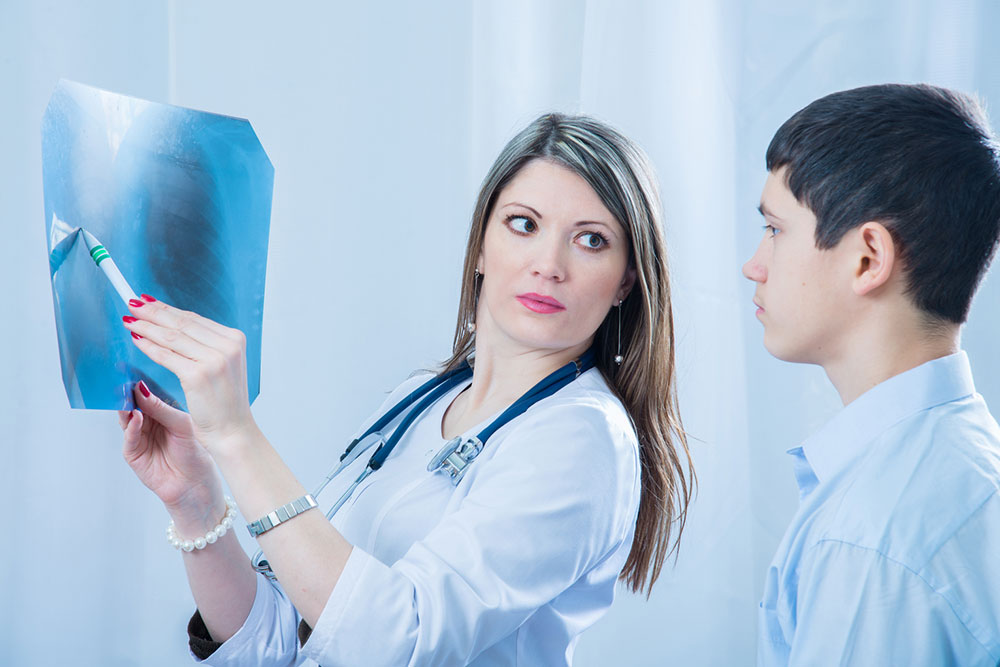
- These tests include imaging tests such as an X-ray, MRI, CT, and PET scans to check for any lumps in the lungs.
- Phlegm analysis helps to detect any cancer cells present in sputum while coughing.
- Further tests include a biopsy, in which a sample of the tissue is taken from the patient to test for cancer cells.
- In some cases, a bone scan is recommended if the doctor suspects that cancer might have spread.
The treatment prescribed for lung cancer depends heavily on the stage the disease has progressed to. In stage1 and stage 2, surgery may be performed to remove the affected part of the lung or the entire lung. This is then followed by chemotherapy. In the advanced stages of cancer, surgery may or may not be performed. Rather, the patient is advised rounds of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy to kill the cancer cells and prevent further spread of the disease in the body.