Main Symptoms for Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that occurs in one or both lungs and is caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other organisms. During this infection, the air sacs become inflamed and they may fill with fluid or pus, causing cough with phlegm or pus, chills, fever, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be contagious and the bacteria and viruses that cause it are usually inhaled. It can be spread through coughing, sneezing, or onto shared objects through touch.
The signs and symptoms of infection usually resemble those of the flu or a cold and tend to vary depending on the pneumonia-causing germs. Below, we outline the main symptoms of pneumonia:
1. Fever
A fever is a common symptom of pneumonia and depending on which germ is responsible for the infection, it could be either mild or severe. An over-the-counter medication should be enough to relieve a mild fever, but it could a few days for the fever to subside. If your fever reaches more than 102 degrees Fahrenheit, you should see your doctor immediately.
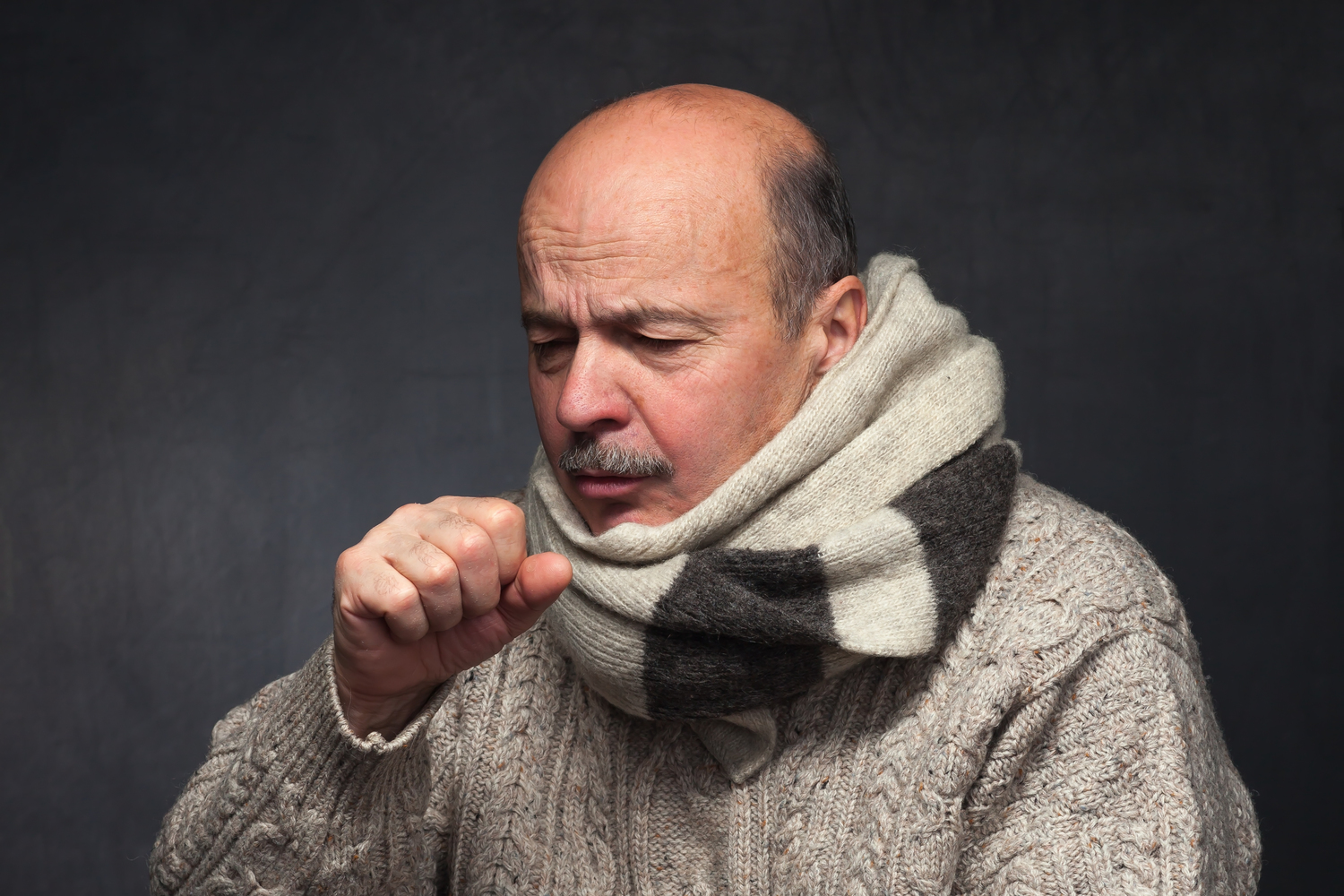
2. Cough
A cough that may or may not produce phlegm is a classic symptom of pneumonia. It is usually the first sign of infection and can last for several days, even after a course of medication is complete. Sufferers may be tempted to treat mild or moderate cough with a cough medicine, but that can hinder the mucus removal that coughing promotes. During a severe pneumonia infection, people may cough up blood which indicates that medical assistance is very much needed.
3. Chills
A pneumonia fever is usually accompanied by body chills. Severe infections can produce sometimes violent shuddering and shaking, which is a sign that the infection is quite severe. This symptom is usually the first to disappear with the help of medicine.
4. Labored breathing
Breathlessness is a main symptom of pneumonia and sometimes this symptom can cause the condition to be misdiagnosed as bronchitis, which produces similar signs. Pneumonia requires different treatment and when labored breathing doesn’t go away with these treatments, your doctor can recommend a chest x-ray which will help distinguish between the two infections.
5. Chest pain
Chest pain experienced with pneumonia occurs as a sharp, stabbing pain or as a dull ache when inhaling and exhaling. This unpleasant symptom is caused by inflammation and as the infection spreads, breathing becomes more difficult and causes chest tightness. Usually, this symptom affects only one side of the chest, depending on the site of the infection.
6. Body aches
Body aches and pains are common after contracting pneumonia. Some patients develop stiffness in their joints while others experience muscle pain. Despite its commonness, doctors are still unsure of their connection to pneumonia. Before self-medicating with over-the-counter painkillers, patients should discuss options with their doctor.
7. Pneumonia in seniors
Eldery people are more susceptible to pneumonia and their infections can be much worse than they are for younger people. Seniors are more likely to get pneumonia due to their weakened immune systems. The symptoms and signs of pneumonia in seniors tend to differ from the general population. An elderly person may experience confusion, disorientation, fatigue, and chest and rib pain. If there are other underlying health issues, it could even lead to pneumonia complications, such as heart failure.
8. Pneumonia in children
Pneumonia is the leading cause of death from infection worldwide in children younger than 5 years of age. Children are at a greater risk of contracting pneumonia because their immune systems are still developing. A mild type of infection caused by a bacterium called mycoplasma pneumoniae and normally referred to as walking pneumonia, is common among school-age children. This type of infection causes milder symptoms and children may not feel sick enough to stay home. Fortunately, walking pneumonia responds well to antibiotic treatments and are rarely serious.