Migraine – Causes, symptoms, and risk factors
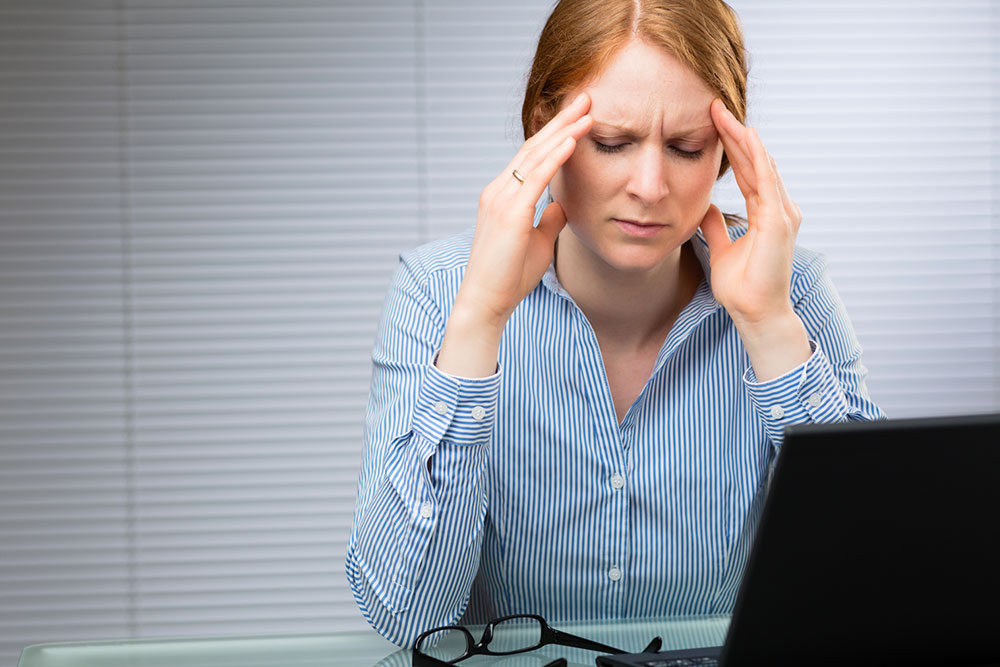
Following sensory warnings among other symptoms, migraine is a condition of intense and recurring headaches that can last for a period of hours or possibly days. The American Migraine Association states that nearly 12% of the population suffers from a migraine; this condition commonly affects people aged between 15 and 55 years. You can also suffer from certain triggers such as sensitivity to light and sound. Some people could also suffer from a minor headache before the migraine attack.
Possible triggers that could cause a migraine
While the exact cause of a migraine is still unknown, researchers have pointed out that the source of this condition is an abnormality in the brain activity. This abnormality changes the way the nerves communicate. If these changes have occurred in the brain, you can be more susceptible to any of the following triggers.
Hormonal changes: More common in women, migraines can be triggered by changes in hormone secretion due to menstruation, menopause, or pregnancy.
Emotional triggers: These triggers include depression, anxiety, shock, excitement, and stress.
Physical causes: An imbalance in the chemicals of the brain due to tiredness, poor posture, and physical overexertion can also serve as a trigger.
Diet: Specific foods such as chocolate, citrus foods, and cheese along with conditions like dehydration and irregular meal timings can trigger the headaches.
Medications: Medications and treatments including sleeping pills and medications used for hormone replacement therapy are also considered as possible triggers.
Environmental triggers
A migraine can sometimes be triggered by experiences such as strong smells, loud noises, and flickering screens. These environmental changes can also include changes in temperature and congested rooms.
Symptoms
While you can experience symptoms before, during, or after the attack, the usual symptoms of a migraine generally include the following:
- Medium or intense pain usually on one side of the head
- Intense throbbing
- Increased straining
- Difficulty in carrying out simple tasks
- Vomiting
- Irritation caused by light and sound
Some people might experience additional symptoms such as sweating, stomachache, changing temperature, and diarrhea.
Risk factors
While migraines can happen to anyone, some factors increase your risk of suffering from a migraine. Some of these factors include the following:
Family history: You might be more prone to developing a migraine if your family has someone that’s already suffering from a migraine.
Age: Generally, migraines occur at an adolescent age. While they get less intense and happen at larger intervals of time with growing age, your migraine might be at its worse in your 30s.
Gender: Compared to men, women are thrice as much susceptible to a migraine. Although, men experience more problems with headaches compared to women during childhood.
Hormonal changes: MIgraine headaches could commence right around the onset of a menstrual cycle. Although they tend to improve with age, migraines could also occur during menopause or pregnancy.
A migraine attack could hamper the quality of life of a person as one would be unable to perform tasks effectively during a migraine attack. If you notice any symptoms of a migraine, you should consult a doctor at the earliest so as to manage the attack effectively.